Difference between revisions of "Audacity Tutorial"
m (→Hints) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
m (→Labeling Tracks) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
====Importing audio==== | ====Importing audio==== | ||
| − | * Go to '''File > Import > Audio... | + | * Go to '''File > Import > Audio...''' and navigate to the audio file that you want to import. Select a file and click '''Open'''. |
* If '''Audacity''' opens a warning screen click the option that says "Make a copy of the files before editing (Safer)" and click '''OK'''. | * If '''Audacity''' opens a warning screen click the option that says "Make a copy of the files before editing (Safer)" and click '''OK'''. | ||
* Audacity can import WAV, AIFF, AU, IRCAM, MP3 and OGG files. WMA files can also be imported with the FFmpeg libraries installed. | * Audacity can import WAV, AIFF, AU, IRCAM, MP3 and OGG files. WMA files can also be imported with the FFmpeg libraries installed. | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
# Go to '''Tracks > Add New > Label Tracks''' | # Go to '''Tracks > Add New > Label Tracks''' | ||
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Edit > Labels > Add Label at Selection (cmd+B)''' |
# Name your label. | # Name your label. | ||
# Use '''Tab''' on your keyboard to select forwards to the next label, and '''SHIFT+Tab''' to select backwards to the previous label. | # Use '''Tab''' on your keyboard to select forwards to the next label, and '''SHIFT+Tab''' to select backwards to the previous label. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:41, 24 June 2020
Audacity is free, open source software for recording and editing audio. It is available for macOS, Microsoft Windows and Linux. Visit the Audacity site to download the application and access additional help documentation and tutorials.Getting Started
Open Audacity from the applications folder.
File Structure
- Audacity has a specific file structure that needs to be maintained.
- Always make a folder to save your Audacity project in.
- Inside your folder there will be the Audacity project file with a .aup extension and a folder ending with _data.
- For example, inside the folder called interview if the project was named October there would be a file called October.aup and a folder called October_data.
- When moving the project between computers always keep the project file and data folder together.
Save your project
- Save the project before doing anything with Audacity.
- Go to File > Save Project As...
- If a warning message appears click OK.
- On the left of the Save window click Desktop.
- Click New Folder in the bottom left.
- Give the folder a meaningful name (your name, name of subject etc) and click Create.
- Give the project a meaningful name in the Save As box.
- Then click Save.
Hints
- As you are working save often. Go to File > Save Project
- When you are done working save the project and quit Audacity. Then copy the entire project folder to a server or external drive.
Importing audio
- Go to File > Import > Audio... and navigate to the audio file that you want to import. Select a file and click Open.
- If Audacity opens a warning screen click the option that says "Make a copy of the files before editing (Safer)" and click OK.
- Audacity can import WAV, AIFF, AU, IRCAM, MP3 and OGG files. WMA files can also be imported with the FFmpeg libraries installed.
Tools
Tracks
Adding Tracks
Tracks > Add new > Audio track, Stereo track, Label track, or Time track
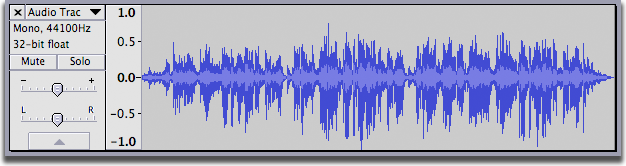
Mono track
-this is one audio file recorded with one microphone
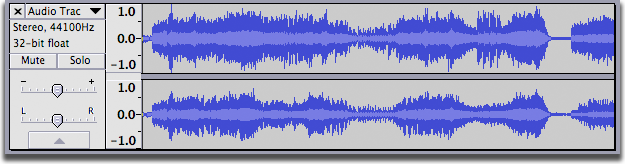
Stereo track
-this is one audio file with a left and right track recorded with a stereo microphone. Stereo tracks can be split into two mono tracks.
Label track
-this track allows you to add markers or regional markers to the whole project or individual tracks
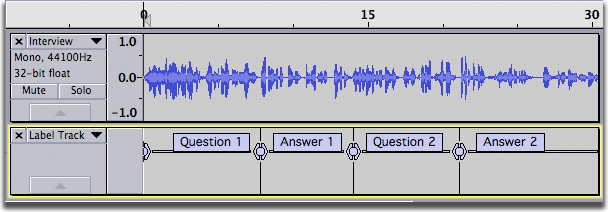
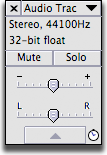
Track Control Panel
Click on the black arrow to view a pull down list of options for each track - allows you to rename the track, provides sample information, waveform view, spectrogram view, mute or solo the track, increase volume and pan left-right function.
Waveform view: vertical axis represents amplitude or loudness and the horizontal axix represents time.
Spectogram view:the horizontal axis represents time, the vertical axis is frequency; a third dimension indicating the amplitude of a particular frequency at a particular time is represented by the intensity or colour of each point in the image.
Editing
Playback
Listen to your project hit the spacebar on your keyboard to Stop or Play
Zooming
Zooming In/Out helps you make accurate selections of your waveform.
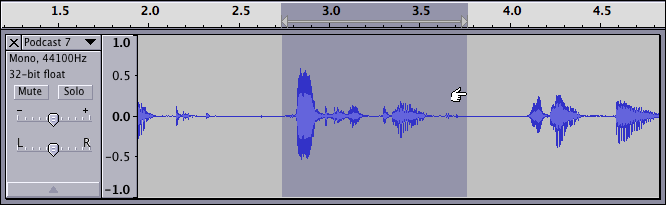
Selection Tool
Highlight a portion of audio using your Selection Tool
![]()
Labeling Tracks
Label tracks and take notes of your project Listen to your audio and make labels.
- Go to Tracks > Add New > Label Tracks
- Edit > Labels > Add Label at Selection (cmd+B)
- Name your label.
- Use Tab on your keyboard to select forwards to the next label, and SHIFT+Tab to select backwards to the previous label.
Editing Audio
- Open a blank track - this will be your working pallet.
- Tracks > Mono track or Stereo Track
- Choose the Selection tool
 in the Tools Toolbar.
in the Tools Toolbar. - Highlight your audio then Edit menu > copy
- Select a point in your empty track then Edit menu > paste
Envelope
Let's you control a tracks volume changes smoothly over time.
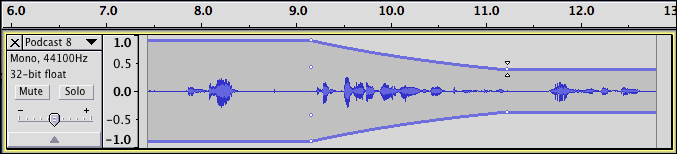
- Select the envelope tool.
- Click a beginning, end, and middle point on your audio waveform.
- Click and hold on a point to increase or decrease the volume.
Effects
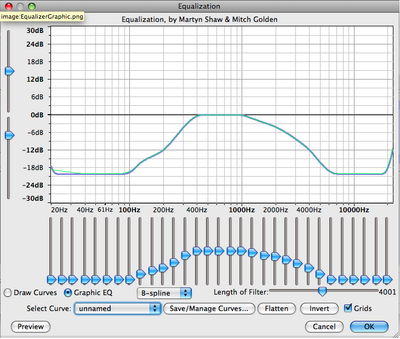
Equalization
Allows you to increase or decrease desired frequencies.
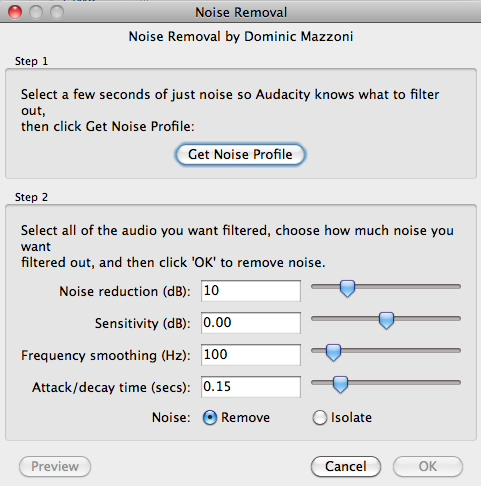
Noise Removal
Removes unwanted background noise.
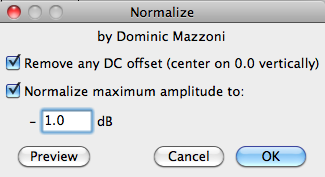
Normalize
Increases the overall volume of your waveform equally.
Exporting
File > Export this command exports the entire project except muted tracks.
File > Export Selection this command exports only selected tracks.
Format:
Select .wav for a high quality uncompressed file but bigger file size.
Select .mp3 for a lower quality, compressed, but small file size.